Table of Contents
Imagine descending in an airplane and your ears suddenly feel blocked, sounds becoming muffled, as if underwater. Now, imagine that sensation lingering long after you’ve landed. This unsettling scenario describes life with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD).
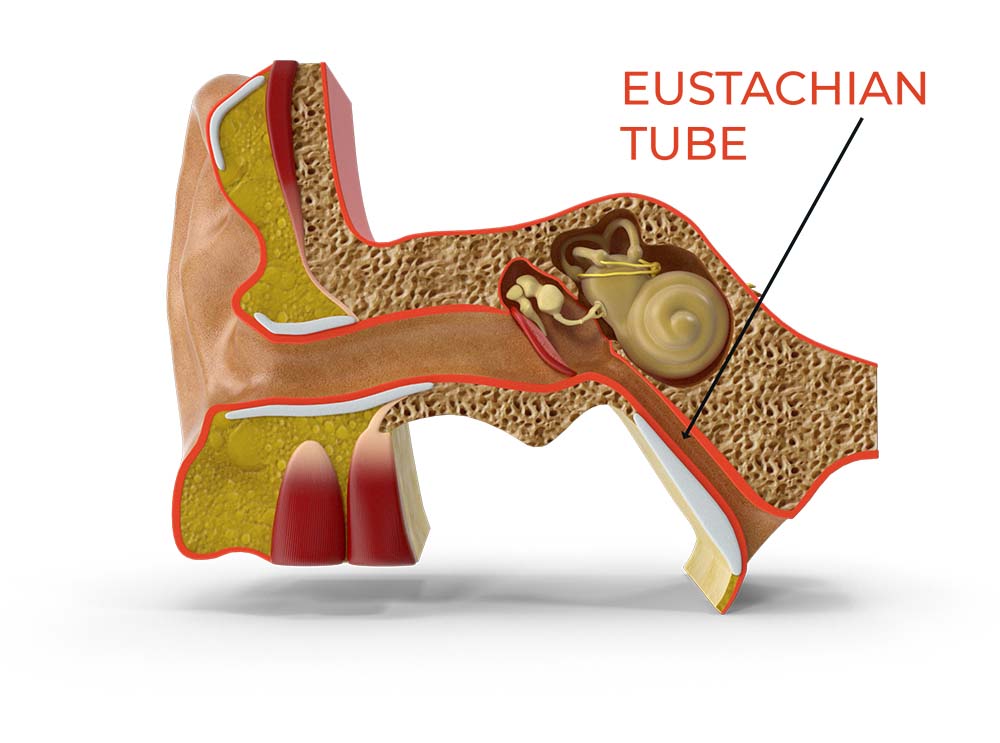
A Tiny Tube with a Big Role: What Is the Eustachian Tube?
Deep inside your ear, behind the eardrum, lies a narrow passageway about 3–4 cm long called the Eustachian tube . You can think of it as the ear’s pressure valve or “secret tunnel” connecting your middle ear to the back of your nose and upper throat. Most of the time, this tube stays closed. But whenever you swallow, yawn or chew, it momentarily opens to perform a vital balancing act.
The Eustachian tube’s job is threefold: ventilation, drainage, and protection . First, it equalises pressure on either side of your eardrum, preventing that unpleasant ear-popping pressure build-up during altitude changes (like when you take off in a plane or drive up a mountain). Second, it drains fluid (and any mucus) from the middle ear into the throat, helping keep the space dry and clear. Third, it protects your ears by keeping out germs and by shielding you from hearing your own internal sounds. In fact, thanks to the Eustachian tube, you’re normally not aware of the sound of your own breathing or voice reverberating inside your head .
In essence, this tiny tube ensures your eardrum can vibrate freely and transmit sound properly . When it’s doing its job, you won’t even notice it’s there. But if it stops working well, the balance is upset – and that’s when problems arise.
When the Ear Feels Off: Symptoms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
How do you know if your Eustachian tube isn’t functioning as it should? The main hallmark is a feeling of blockage or fullness in the ear, often accompanied by muffled hearing – many people describe it as feeling like they’re underwater . Sounds may seem distant or muted. You might find yourself asking others to repeat themselves or turning up the TV, only to realize the issue is in your ear, not the volume.
Other common symptoms include:
Ear pressure or pain: Because the middle ear can’t equalise pressure, the eardrum may get stretched inward, causing discomfort or even pain . (Typically this is a dull, intermittent pain; severe or constant ear pain is usually due to other causes.)
Popping, clicking or crackling noises: You may hear occasional pops or crackles as the tube tries to open or when it finally does briefly open. Some people experience frequent popping sounds when swallowing or yawning.
Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing): A blocked Eustachian tube can lead to tinnitus or a whooshing sound in the affected ear . This ringing usually comes along with the feeling of fullness and muffling, rather than occurring alone .
Mild dizziness or balance issues: Your middle ear also affects balance, so ETD can sometimes make you feel slightly dizzy or unsteady . It’s usually mild vertigo, if any – more of an “off-kilter” feeling.
Hearing your own voice loudly (autophony): Interestingly, there’s a less common form of ETD where the tube stays too open (called patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction). In that case, instead of muffled hearing, you might hear your own voice or breathing echoing in your ear unnaturally loud . This can be quite disconcerting – imagine speaking and feeling like you’re in a cave with your voice bouncing back at you.
Any combination of these symptoms can occur. One or both ears may be affected. You might notice symptoms are worse when you have a head cold or during changes in altitude. In mild cases, the issue is fleeting – perhaps lasting only hours or a few days. In other cases, especially if underlying causes persist, the problem can linger for weeks or longer . If you’ve had a “stuffy ear” that refuses to clear after more than a week or two, it’s a sign you may be dealing with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction rather than just temporary “airplane ear.”
What Causes ETD?
The culprits behind ETD typically involve blockage or inflammation. Common causes include:
Colds and Flu: Upper respiratory infections often leave behind inflammation, temporarily blocking the tube.
Allergies: Seasonal allergies or dust mites can lead to chronic nasal congestion, affecting tube function.
Altitude Changes: Rapid pressure changes, like those in airplanes or mountains, can trigger temporary dysfunction.
Smoking: Smoke irritates nasal passages, increasing ETD risk significantly.
Acid Reflux: Acid irritation from chronic reflux can inflame the tube’s opening.
How is ETD Diagnosed?
Diagnosing ETD usually involves a straightforward examination:
Visual Inspection: Examining the ear canal and eardrum.
Tympanometry: A painless test measuring eardrum movement.
Eustachian Tube Function Test: A brief, gentle pressure test assessing how well the tube opens.
These tests help identify whether ETD is present or if another issue is causing your symptoms.
Effective Solutions for ETD
Thankfully, most ETD cases respond well to simple solutions:
Home Remedies: Swallowing, yawning, chewing gum, or gentle pressure manoeuvres (like Valsalva) can quickly relieve mild cases.
Decongestants and Antihistamines: Short-term use of nasal sprays or allergy medications can alleviate congestion and inflammation.
Nasal Steroids: For chronic sufferers, steroid sprays can effectively manage long-term inflammation.
Medical Procedures: Persistent ETD might require minor procedures like balloon dilation of the Eustachian tube or insertion of ventilation tubes (grommets) for ongoing relief.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Prevention often involves proactive management:
Manage allergies proactively.
Avoid smoking or smoky environments.
Stay hydrated to maintain thin mucus.
Use ear pressure equalising techniques during flights or altitude changes.
Clear Ears, Clearer Life
Living with blocked ears or muffled hearing can be profoundly frustrating. Fortunately, solutions are accessible and effective. If you recognise these symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek a professional evaluation.
At Audiocare, we’re equipped with advanced assessments to pinpoint your condition and recommend personalised treatments. Life’s sounds deserve to be heard clearly – book an evaluation today and step out from underwater into a clearer, brighter auditory experience.
References
Cleveland Clinic: Informações abrangentes sobre a Disfunção da Trompa de Eustáquio, incluindo sintomas, causas e tratamentos. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22527-eustachian-tube-dysfunction
Patient.info: Discussão detalhada sobre a Disfunção da Trompa de Eustáquio, abordando sintomas, causas e opções de tratamento. https://patient.info/ears-nose-throat-mouth/earache-ear-pain/eustachian-tube-dysfunction
Johns Hopkins Medicine: Informações sobre a Disfunção da Trompa de Eustáquio, incluindo causas e tratamentos. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/eustachian-tube-dysfunction
NHS Inform: Informações sobre a Disfunção da Trompa de Eustáquio, incluindo sintomas, causas e tratamentos. https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/ears-nose-and-throat/eustachian-tube-dysfunction









